|
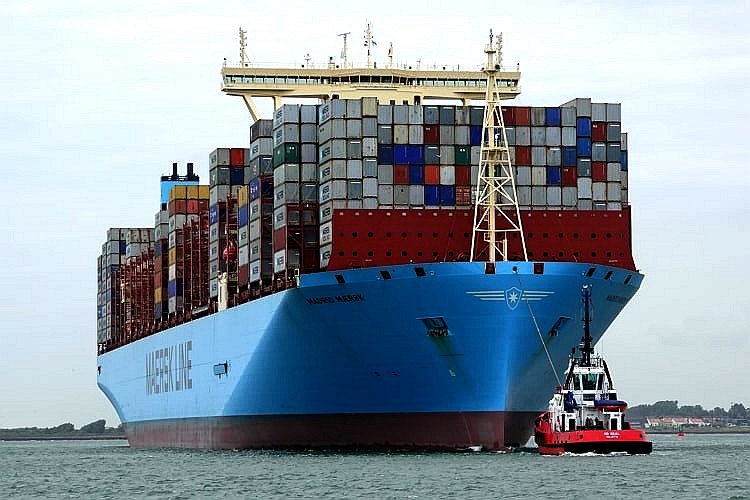
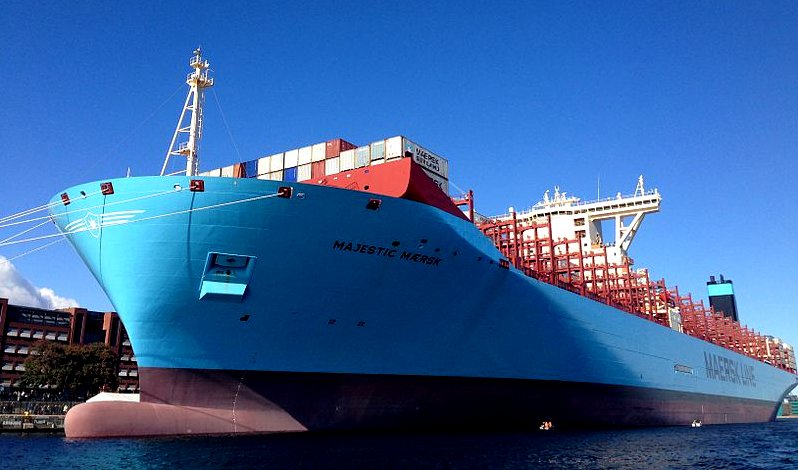
MAERSK MADRID CONTAINER SHIPS 5th
ABOUT - CLIMATE CHANGE A-Z - CIRCUMNAVIGATION - CONTACTS - DONATE - FOUNDATION - HOME - OCEAN PLASTIC A-Z Please use our A-Z INDEX to navigate this site
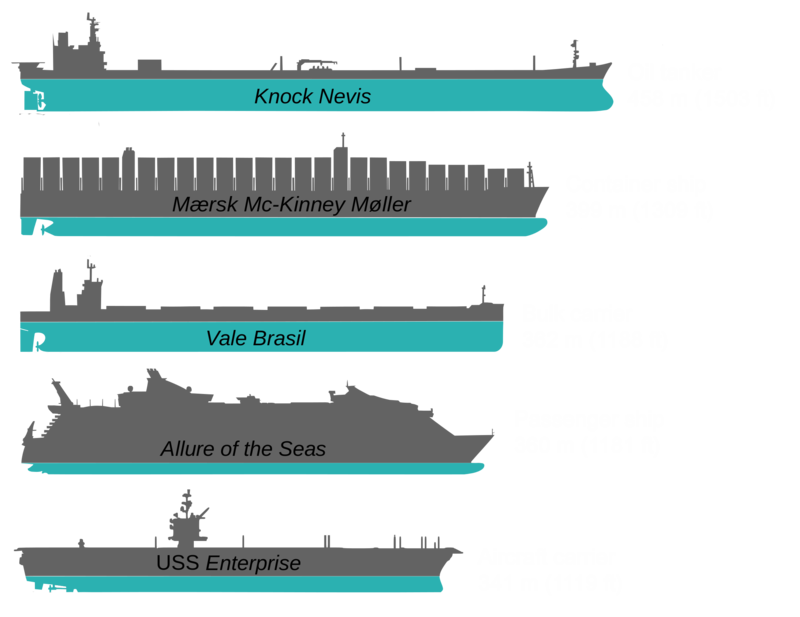
MAERSK MADRID - This South Korean built mammoth fossil fueled vessel was constructed by Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering.
5. MAERSK MADRID
The
Madrid Maersk was the second-largest container ship to surpass the
20,000 TEU mark next to MOL Triumph. It is the biggest Maersk ship
up until October 2019. It is the first of eleven second-generation Maersk Triple E-class
container ships. Built by Daewoo Shipbuilding
& Marine Engineering in Okpo Shipyard, South Korea with a container carrying capacity of
20,568 TEU.
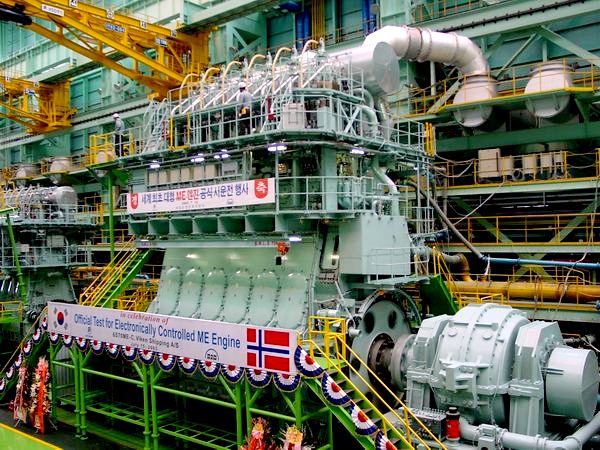
TWIN ENGINES
Unlike conventional single-engined container ships, the new class of ships has a twin-skeg design: it has twin diesel engines, each driving a separate propeller. Usually, a single engine is more efficient, but using two propellers allows a better distribution of pressure, which increases the propeller efficiency more than the disadvantage of using two engines.
SPECIFICATIONS
Capacity: 18,270
TEU DWT:
210,019 tonnes Fuel consumption:
168 g/kWh (21,200 gallons per day)
THE MARKET
Maersk planned to use the ships on routes between Europe and Asia. In 2008 there was a reduction in demand for container transport caused by recessions in many countries. This left shipping lines in financial difficulties in 2009, with surplus capacity.
Some ships were laid up or scrapped. However, there was a sudden resurgence of demand for container transport in 2010; Maersk posted its largest ever profit, and orders for new ships increased, leading to fresh concerns about future overcapacity. The market was still characterized by overcapacity and decreasing prices for new ships in 2013.
China Shipping Container Lines ordered five ships with a capacity of 18,400 TEU from Hyundai Heavy Industries, topping the Triple E class, with delivery from late 2014. United Arab Shipping Company has ordered (also from Hyundai) five slightly larger ships and five ships larger than the Maersk E class. Several other larger ships have been ordered by the industry.
Slow steaming, as used by the Triple E class, is one way of managing capacity and reducing fuel consumption. The order for many big ships is a gamble on Maersk's part that Chinese exports will continue to grow. Lack of market growth in the second half of 2012 caused Maersk to postpone a decision on how to use the Triple E class. Five Triple E-class vessels were to be delivered in 2013, with an impact sometime in 2014 with eight or nine Triple E-class vessels operating.
Maersk already used approximately 100 ships on the Asia-Europe route, which is their most important. SeaIntel expects about 46 ships with more than 10,000 TEU each to be delivered worldwide in 2013. The construction of newer, larger ships has influenced development plans at ports such as London Gateway and JadeWeserPort in Wilhelmshaven (Germany), and Algeciras and Tanjung had bigger cranes installed. The maximum number of TEUs carried in one trip was 18,024 in January 2015, in Algeciras, Spain.
STANDARD
Modern containers ships are cargo ships designed to carry their cargo in standardized steel boxes, using a technique called “Containerization”. This type of ocean transport contributes about 90% of non-bulk cargo movement worldwide. This is how you get your televisions, computers, fruits and spare parts. Cars are generally transported by ferries, though some collector vehicles are delivered in containers.
Fossil fuelled container ships that belch clouds of fumes as they ply the ocean may one day be a thing of the past. Shipping will continue without those who fail to adapt to changing circumstances such as global warming and zero carbon fleets by 2100, as part of the IMO's ocean cleanup objectives. In the meantime here are the top ten biggest gas guzzlers and potential ocean polluters in the world @ October 2019.
Why
Are They So Big?
The use of fossil fuels raises serious environmental concerns. The burning of fossil fuels produces around 21.3 billion tonnes (21.3 gigatonnes) of carbon dioxide (CO2) per year. It is estimated that natural processes can only absorb about half of that amount, so there is a net increase of 10.65 billion tonnes of atmospheric carbon dioxide per year. Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas that increases contributes to global warming. A global movement towards the generation of low-carbon renewable energy is underway to help reduce global greenhouse gas emissions.
SIX STEPS TOWARD A COOLER PLANET
1. TRANSPORT: Phase out polluting vehicles. Governments aim to end the sale of new petrol, and diesel vehicles by 2040 but have no infrastructure plan to support such ambition. Marine transport can be carbon neutral with development..
2. RENEWABLES: Renewable energy should replace carbon-based fuels (coal, oil and Gas) in our electricity, heating and transport.
3. HOUSING: On site micro or macro generation is the best option, starting with new build homes to lock carbon.
4. AGRICULTURE: We need trees to absorb carbon emissions from a growing population, flying, and to build new homes. Reducing food waste and promoting less energy intensive eating habits such as no meat Mondays.
5. INDUSTRY: Factories should be aiming for solar heating and onsite renewable energy generation.
6. POLITICS: - National governing bodies need to adopt rules to eliminate administrative wastages, to include scaling down spending on war machines, educating the public and supporting sustainable social policies and financing that mesh with other cultures.
These marvels of engineering excellence got us where we are today, technology wise, but threaten to destroy the planet if we do not adapt in time to repair at least some of the damage we have done.
FOSSIL
FUEL HEALTH HAZARDS
One of the world's largest diesel engines being assembled in Japan.
1995 COP
1,
BERLIN, GERMANY
2022 COP 26 - Will they have applied the brakes?
LINKS & REFERENCE
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fossil_fuel https://www.studentenergy.org/topics/fossil-fuels
EXTINCTION OF SPECIES - From blue planet to scorched earth because vested interests prevented politicians from putting the brakes on. Economics stopped them thinking about the safety of life on earth, including the future of our children. They'd rather die richer, than live, gambling with the lives our their offspring and every other species on planet earth.
Please stop playing with fire, there is no Planet B.
HOW MUCH IS THE EARTH HEATING UP - As of early 2017, the Earth had warmed by roughly 2 degrees Fahrenheit (more than 1 degree Celsius) since 1880, when records began at a global scale. The number may sound low, but as an average over the surface of an entire planet, it is actually high, which explains why much of the world’s land ice is starting to melt and the oceans are rising at an accelerating pace. If greenhouse gas emissions continue unchecked, scientists say, the global warming could ultimately exceed 8 degrees Fahrenheit, which would undermine the planet’s capacity to support a large human population.
This website is provided on a free basis as a public information service. Copyright © Cleaner Oceans Foundation Ltd (COFL) (Company No: 4674774) 2019. Solar Studios, BN271RF, United Kingdom. COFL is a charity without share capital.
|